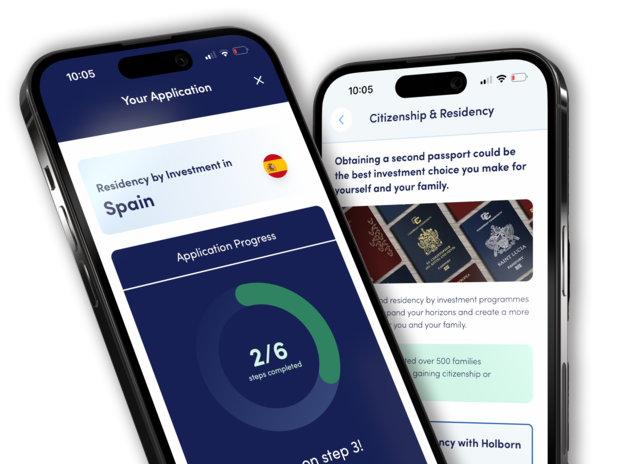
Get the Holborn App
Track your applications from start to finish

Opening up a world of opportunity
Citizenship and residency by investment programmes allow you to expand your horizons and create a more secure future for you and your family
Benefits of Second Citizenship
Visa-Free Travel
A second passport grants increased global mobility, allowing visa-free travel to over 180 countries across the globe.
Business Opportunities
Residency and citizenship by investment programmes allow you to increase your business footprint on an international scale. Travel becomes more manageable, allowing you to focus on your business goals.
Save Time
A golden visa can save time, helping you avoid travel complications such as lengthy visa application processes.
Back-up Plan
Having a Plan B is becoming an increasingly important aspect to consider. Gaining second citizenship or residency through an investment programme gives you and your family an effective backup plan and greater flexibility.
Tax Benefits
Most citizenship and residency by investment programmes are in low-tax jurisdictions or offer particular tax advantages. These benefits include savings on Income Tax, Wealth Tax, Inheritance Tax and Capital Gains Tax.
Live, Work and Study
Golden visa programmes can open up a wealth of opportunities. By making a qualifying investment, your family have the right to live, work and study in your chosen country.
Benefits of Second Citizenship
Visa-Free Travel
Business Opportunities
Save Time
Back-up Plan
Tax Benefits
Live, Work and Study
Find out more
Working with Holborn
Holborn Pass is an international leader in investor visas. Through our global partnership with prestigious law firms, developers and financial institutions, we provide comprehensive residency and citizenship solutions.
We are a part of the wider Holborn Assets Group, a leading financial services company with a global footprint. Established in 1998, Holborn Assets supports over 20,000 clients, managing more than $2 billion of assets.
Our core values are integrity and transparency. Whether it’s increased global mobility, developing business opportunities or creating a more secure future for their family, helping our clients pursue their goals is at the forefront of what we do as a business.
Holborn’s expert team provides a bespoke, end-to-end service and tailored advice designed to support the client’s needs and aims. We have successfully helped hundreds of individuals and families secure a golden visa, opening up a world of opportunities and possibilities.
Working with Holborn
We have helped over
1000+
families to gain citizenship or residency
Over
$300 million
invested in CBI programmes through us
More than
$450 million
of property assets purchased in the last three years
We have helped over
40
client nationalities secure a golden visa
1000+
Families helped to gain citizenship/residency
$300 million
Amount we have invested in CBI programmes
$450 million
Value of property assets purchased in the last three years
40+
Client nationalities we have helped secure a golden visa
Loading...

“We worked with Jonathan at Holborn Assets for the last month, He has been very tentative to many of our questions and diligently setting up important meetings for us during our trip...”
David
Read our guide to Citizenship & Residency by Investment



Guide to Citizenship & Residency by Investment
In this guide you'll discover everything you need to know about how these programmes work, their benefits, the key destinations, and why Holborn Pass is the ideal partner for your investment migration journey.